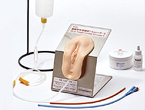
M193-1


Main body unit weight/ 1.7kg
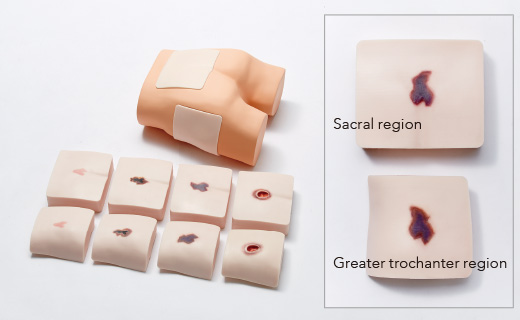
Main unit parts [sacral blocks] / Qty.: Set of 5 types / Weight: 6.5 kg / Size 180 (W) x 160 (D) x 55 (H) mm
[Greater trochanter blocks] / Qty.: Set of 5 types / Weight: 4.2 kg / Size 160 (W) x 150 (D) x 55 (H) mm
Accessories / Baby powder
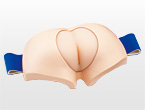
M193-2


Main body unit weight/ 1.7kg
Main unit parts/ 1 sacral block (normal)、1 greater trochanter block (normal)
Total weight/2.2 kg
Accessories / Baby powder

M193-3


Main body unit weight/ 1.7kg
Main unit parts [sacral blocks] / Qty.: Set of 5 types / Weight: 6.5 kg / Size 180 (W) x 160 (D) x 55 (H) mm
[Greater trochanter blocks] / Qty.: Set of 5 types / Weight: 4.2 kg / Size 160 (W) x 150 (D) x 55 (H) mm
Accessories / Baby powder

General name: General use diagnostic ultrasound imaging system(407061000)
Medical equipment class: Controlled Medical Device, Specially Designated Maintenance Required Medical Device
Product name: SonoSite M Series Medical device authentication number: 219ADBZI00197000
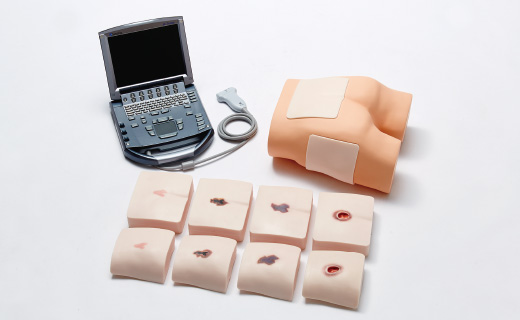
Overview (M193-2)
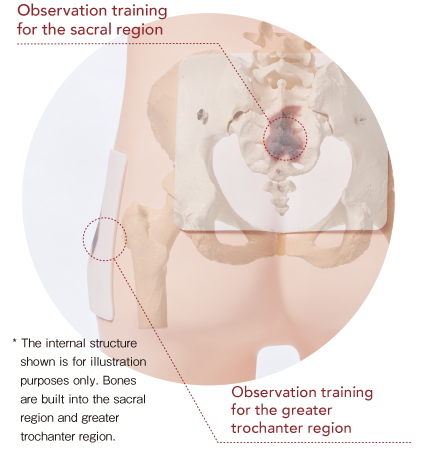
For basic training to understand the internal structure of skin and subcutaneous tissue where bed sores can easily occur and for operation of ultrasonograph equipment
Built-in bone and muscle structures in places closely linked to bed sores. Ideal for concentrated training to understand the internal structures relating to bed sores.
1 Checking the area
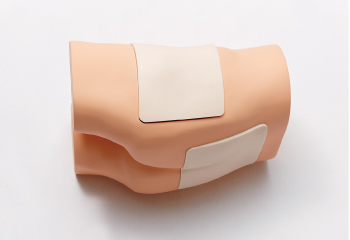
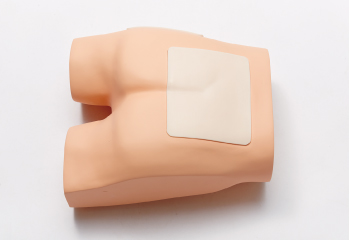
Lateral position for the greater trochanter region, and prone position for the sacral region. It is possible to carry out confirmation training for areas where bed sores can easily occur.
| Greater trochanter region |
|---|
 |
| Sacral region |
 |
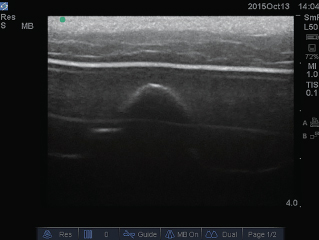
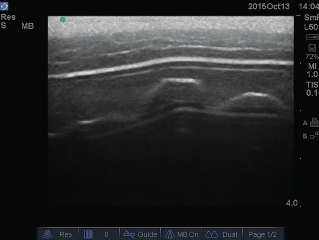
2 Extraction of minor axis and major axis
It is possible to project the optimum images from the minor axis and major axis and all other directions.
 |
| Minor axis |
|---|
 |
| Major axis |
 |
 |
 |
Overview (M193-2)
Training to understand a variety of different bed sore types
at two points where DTI can easily occur
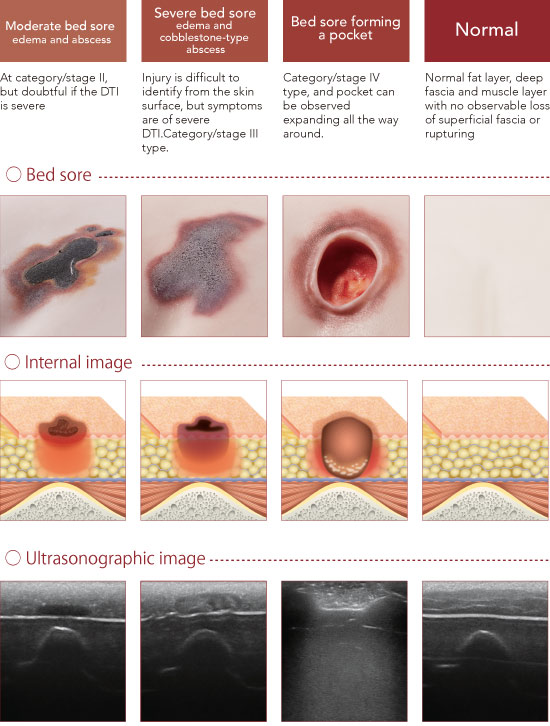
Training for observation of symptoms for the following four typical patters at the sacral region and greater trochanter region can be carried out: "Mild bed sores: edema and hypoechoic areas",
"moderate bed sores: edema and abscess",
"severe bed sores: edema and cobblestone-type abscess" and "pocket-type bed sore".
 |
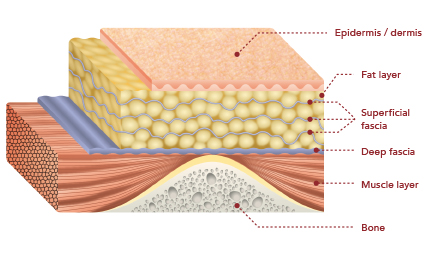
This model recreates the structure of the fat layer
in the gluteal area where bed sores can easily occur.
Illustration of the bed sore internal structure of the training phantom
for ultrasonic observation of tissue injuries
 |
Testimonial for the training phantom
for ultrasonic observation of tissue damage
Professor Hiromi Sanada
Department of Gerontological Nursing/Wound Care Management, Division of Health Sciences and Nursing, Graduate School of Medicine, University of Tokyo
The world's first training phantom for deep tissue injuries has been successfully created, combining knowhow regarding ultrasonography diagnosis which has been developed for the early detection of deep tissue injuries and for preventing the damage from progressing, with Sakamoto Model's technology which recreates the same sensation as that of actually touching the skin and the feeling of an actual clinical procedure.
The incidence of bed sores has been decreasing in Japan, but with the rapid increase in the elderly population, it is predicted that the number of bed sores will begin to increase on a continuous basis.In Japan in particular, where comprehensive community care systems are actively being promoted, I think it will become increasingly important for nurses who are engaged in home nursing or specialized care activities to be able to prevent deep tissue injuries (DTI) such as bed sores which are not visible to the naked eye by carrying out early detection.
For these reasons, it is essential to have solid training in the operation of ultrasonography equipment, to be able to understand ultrasonography images of bed sores, and particularly to understand deep tissue injuries. I feel that this training phantom is an indispensable training tool.
You can carry out the same training in the operation ofultrasonography equipment as with normal models, and also carry out training in ultrasonography scanning and deepen your understanding of deep tissue injuries using the four typical patterns which appear in the sacral region and greater trochanter region where deep tissue injuries can easily occur, namely loss of superficial fascia, hypoechoic areas, abscesses and cobblestone-type lesions.Compared to ultrasonography images of the complex human body, it is much easier to spot and recognize deep tissue injuries during training.Also, the five blocks can be replaced in the lower body easily without the need for any heavy lifting.
Finally, we can expect many of the medical staff involved in providing nursing care and treatment for bedsores to be able to learn about ultrasonography using this training phantom.
Movie
Feature
Mild bed sore: edema and hypoechoic areas
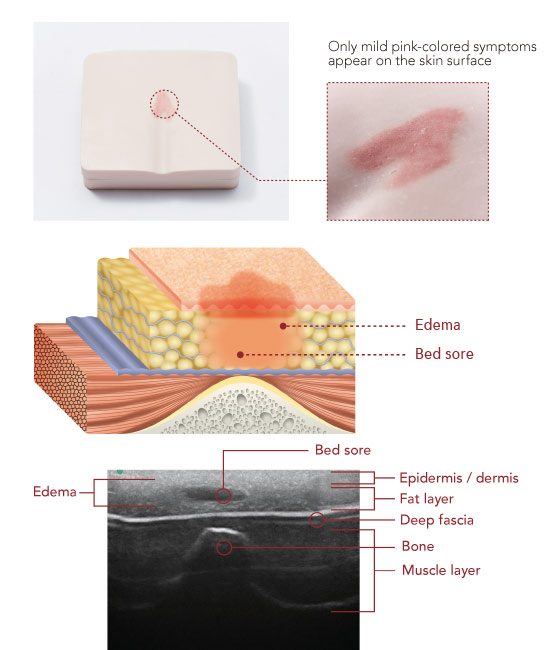
Observing features such as loss of superficial fascia, localized areas of low brightness, and the location and depth of abnormal findings make it possible to confirm mild bed sore at category/stage I to II.
 |
 |
Storage box
 |
●Body case…Weight: 2.5kg / Size 530 (W) x 430 (D) x 475 (H) mm ●Block case…Weight: 2.2kg / Size 530 (W) x 430 (D) x 135 (H) mm |